What is FlatFile?
A simple text file having data in text format(non formatted text) is called flatfile , flatfiles are used since the advent of computers in business and still they are used widely.
Two Types of flatfiles we can use in webMethods,
1. With No record identifier.
2. With record identifier.
1.With No record identifier
How many different types of flatfiles are there based on record parsing methods?
Flatfiles can be broadly classified into three different types based on the type of their record parsing methods , these three types are :-
1)Delimited FlatFile
2)Fixed length FlatFile
3)Variable length FlatFile
Again Flatfiles can be divided into two different types based on the type of field extractors , these are :-
1)Fixed length
2)Nth field
In Fixed length extractor type each field is defined by its starting index and end index , in this case the length of the field will be constant for every record.
In Nth field extractor the field is extracted by the position of the field , such as 0,1,2 . the position starts from 0. This is the most widely used extractor type for the flatfiles because it does not limit the size of the field as in the case of Fixed length extractor.
Delimited FlatFile :- In these kind of FlatFiles , the records are separated by some kind of delimiters such as newline,pipe(|),tab etc. The field extractor can be any of the two i.e fixed length or Nth field extractor.
Now we can see Delimited FlatFile with the following screen shots,
First create a text file with the data like below,
Data in the Text file will be like this,
Before going to create flatfile just look out the definitions of FF dictionary and FF Schema
Flatfile dictionary:- Flatfile dictionaries are created as namespace elements in the Integration Server and contain definitions of records, composites, and fields. When you change a definition in a flatfile dictionary that is referenced in multiple flatfile schemas, the element definition is updated automatically in all of the flatfile schemas.
Flatfile Schema:- To communicate using flatfiles, we have to create a flatfile schema that contains a particular flatfile’s structural information, including how to identify records and separate those records into fields.
Create flatfile dictionary
Right click on folder select new and select Flat File Dictionary
Give name to the dictionary and click finish
Select delimiter(most of the cases we use delimiters only) and give the fields as per text document
Record :- Record is seperated by ';' type ';' otherwise if you don't give any record ended then simply give new line.
Field:- Field is ended with ','
subfield:- is given as ':'
Quoted Release Character :- Quoted release character is used to keep the section of a flat file as it is mentioned in the flat file , any delimiters included within the quoted release character will not be counted.
Then click on FlatFile Structure tab and go to properties browse on set
And select dictionary then click on next and then finish and save.
Up to above steps flatfile schema is completed successfully.
Now create one flow service and invoke wmpublic----> pub ---> file ----> getfile service
A simple text file having data in text format(non formatted text) is called flatfile , flatfiles are used since the advent of computers in business and still they are used widely.
Two Types of flatfiles we can use in webMethods,
1. With No record identifier.
2. With record identifier.
1.With No record identifier
How many different types of flatfiles are there based on record parsing methods?
Flatfiles can be broadly classified into three different types based on the type of their record parsing methods , these three types are :-
1)Delimited FlatFile
2)Fixed length FlatFile
3)Variable length FlatFile
Again Flatfiles can be divided into two different types based on the type of field extractors , these are :-
1)Fixed length
2)Nth field
In Fixed length extractor type each field is defined by its starting index and end index , in this case the length of the field will be constant for every record.
In Nth field extractor the field is extracted by the position of the field , such as 0,1,2 . the position starts from 0. This is the most widely used extractor type for the flatfiles because it does not limit the size of the field as in the case of Fixed length extractor.
Delimited FlatFile :- In these kind of FlatFiles , the records are separated by some kind of delimiters such as newline,pipe(|),tab etc. The field extractor can be any of the two i.e fixed length or Nth field extractor.
Now we can see Delimited FlatFile with the following screen shots,
First create a text file with the data like below,
Data in the Text file will be like this,
Flatfile dictionary:- Flatfile dictionaries are created as namespace elements in the Integration Server and contain definitions of records, composites, and fields. When you change a definition in a flatfile dictionary that is referenced in multiple flatfile schemas, the element definition is updated automatically in all of the flatfile schemas.
Flatfile Schema:- To communicate using flatfiles, we have to create a flatfile schema that contains a particular flatfile’s structural information, including how to identify records and separate those records into fields.
Create flatfile dictionary
Right click on folder select new and select Flat File Dictionary
Now create a Field definition as per the text file in my assumption i created like this
Right click on field definition and click on new
give name of the first field in my case that is EmpNo like wise create EmpName and salary
we have a composite fields in our text file i.e., Address and it has 2 sub fields(area and city)
So we have to create composite field definition and sub fields for this
right click on composite definition and click on new
Give name to the field and click finish
Now create the sub fields for area and city
Right click on Address and click new
In this select field definition
Give Extractor type as Nth field because here there is no fixed positions in the text file and give names as according to text file data in my case area:city
positions are starts from 0,1,2... and click finish
Now create Record definition meaning you have to give one name to the text file data like in database table name
for example: employeedetails
And then click on EmployeeDetails then click on new we can see below screen
Already we created the field definition so click on field reference and click next
Select the dictionary which already created and click next
Select the field name which already created in field definition, those will appear in the screen only when you save the dictionary and click next
Give Extractor type as Nth field and positions are starts from '0' and in my case position '0' is EmpNo and '1' is EmpName and so on
Then click finish
Like field reference select composite reference also which already created in composite definition and click next.
select address and click next
give position (continue positions from field reference already i gave 0,1,2 so now giving 3) and click finish. so the flatfile dictionary is created successfully.
Now lets see how to create schema
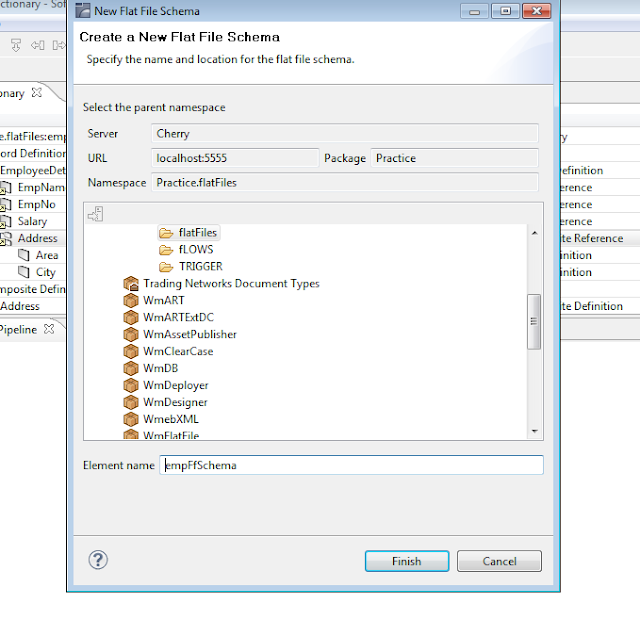
right click on flatfile folder and the click on new flatfile schema and give name then click finish
Record :- Record is seperated by ';' type ';' otherwise if you don't give any record ended then simply give new line.
Field:- Field is ended with ','
subfield:- is given as ':'
Quoted Release Character :- Quoted release character is used to keep the section of a flat file as it is mentioned in the flat file , any delimiters included within the quoted release character will not be counted.
Then click on FlatFile Structure tab and go to properties browse on set
 |
| and then finish and save. |
Now create one flow service and invoke wmpublic----> pub ---> file ----> getfile service
then goto pipeline double click on filename and give fullpath of the file location including name as mentioned above screen shot.
And then click OK.
Again double click on loadAs and select as bytes then click OK
invoke one more service to convert flatfile to document it is located in wmFlatFile ---> pub---->flatFile---->convertToValues service
Then go to pipe line and double click on ffSchema and give full location of ffschema which we created in designer. for eg: Practice.flatfiles:empFFSchema then click ok and then ok.
Now goto pipeline and map bytes to ffdata
Now run the service like below
Right click and click run as and click run flow service and one more screen will appears as there is no input like that just click ok.
Now you will get result like below
Will continue record with ID also later....